Ukrainian budgetary and state institutions continue ordering accounting programs UBS, KBS, BAS, and UA-Budget, which presumably only imitate Ukrainian products. It seems that they continue functioning on the core of the russian sanctioned 1C without guarantees that the aggressor state does not have access to user data.
Since the beginning of the full-scale invasion, Ukrainians have begun to react more sharply to any products related to russia. The IT field was no exception, in particular, accounting programs.
Until recently, the most popular software in this segment was 1C — the development of a russian company designed to create enterprise automation systems. In spring 2017, the NSDC imposed sanctions on the products of the developer of this platform, banning it from selling its products on the territory of Ukraine.
1C as a donor for other programs, and why it is dangerous
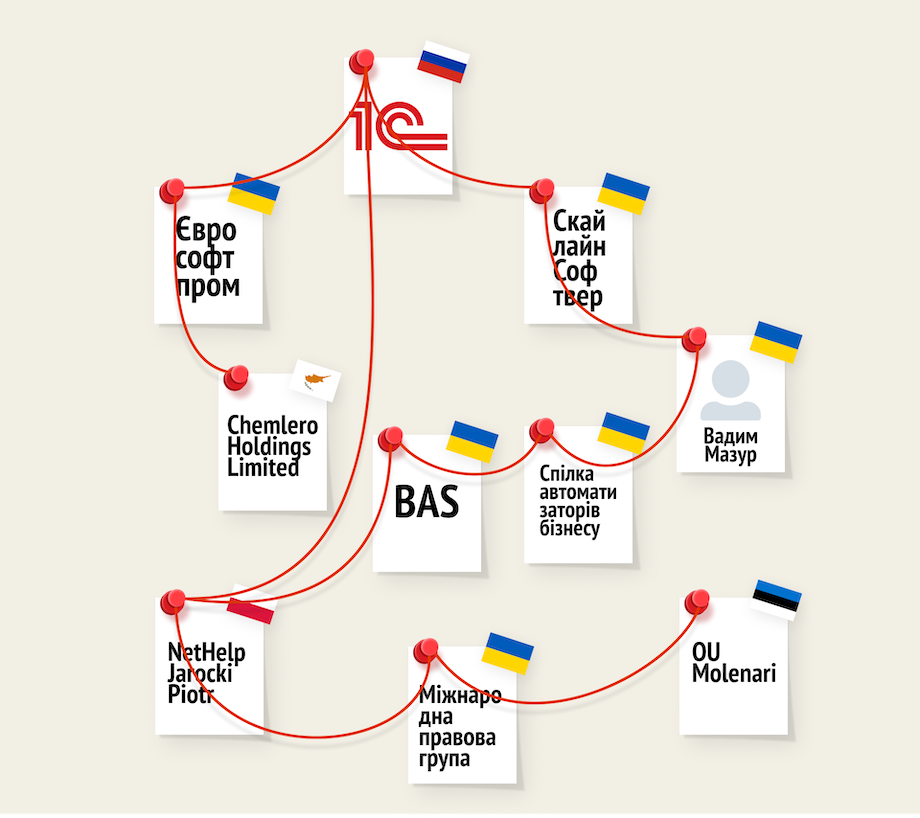
Until 2017, 1C in Ukraine was sold and supported by two companies: SE Eurosoftprom and Skyline Software. The first one owns the copyrights to 1C in our country, the other one coordinates the maintenance, revision, and distribution of the program. Both were sanctioned.
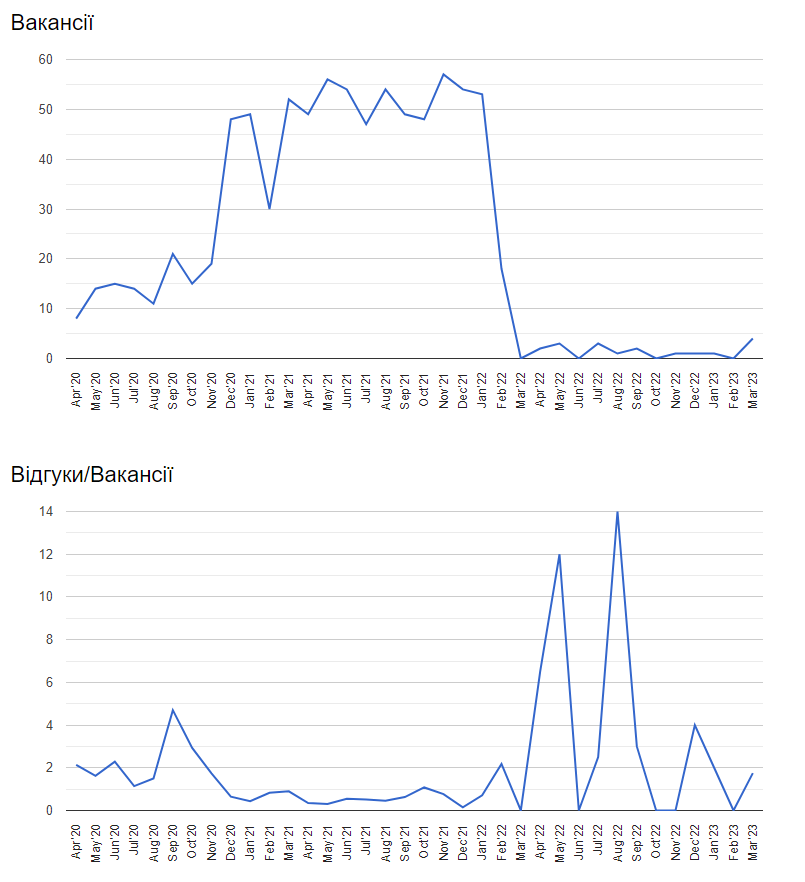
After the introduction of restrictions, the actual use of 1C in the country has not ceased. This is confirmed by the data of the Ukrainian community of DOU programmers, according to which, during 2021, approximately 60 vacancies related to 1C were posted on DOU on a monthly basis.
To circumvent the restrictions, the technological solutions of 1C were transferred to the BAS system, which is based on the 1C architecture. This was confirmed by Piotr Jarocki, a representative of the Polish company NetHelp, which owns the BAS trademark, in a commentary to DOU.
In addition, Public Organization Union of Business Automation supports and maintains BAS products in Ukraine. It provides support to users of business automation programs through the ITS (Information Technology Support) agreement. It is still stacked through a site on the subdomain 1c.ua, as well as its mirror on bas-soft.eu.
Vadym Mazur, the head of the Union of Business Automation, a citizen of Ukraine, is also the founder and director of the above-mentioned Skyline Software. Read more about the transfer process and relations with russian beneficiaries in the DOU investigation.
In addition, in 2020, the NSDC expanded the sanctions list and added BAS and UA-Budget products to it.
The SSU explained in response to a DOU request why the use of programs developed in russia is dangerous:
“The use of software products by state institutions, to which special economic and other restrictive measures (sanctions) are applied, creates a real threat to the confidentiality, integrity, and accessibility of data circulating in automated systems.”
In particular, thanks to such products, information about user companies can be collected to undermine the country’s economy.
How much procuring entities spend on prohibited programs
Despite the decision of the NSDC, confirmed relations, the investigation published in April last year, and a clear danger, Ukrainian procuring entities concluded contracts for the supply of BAS customer packages worth more than UAH 5 mln on Prozorro during the full-scale invasion. Orders provide for the installation of licensed software, consultations on the use of the system, the supply of copies of the system, the provision of licenses to programs, as well as access to online services and updates to automated systems. The program “BAS Client License” is also used by Suspilne. Thus, on May 15, JSC Public Broadcasting Company of Ukraine signed an agreement for UAH 177,600 for a set of programs for 70 employees.
The banned UA-Budget was also purchased after February 23, 2022, but on a smaller scale. Thus, Prozorro contains information about more than 50 such contracts worth about UAH 900,000. The list includes the supply of software packages of this system, their support, maintenance and technical support, access to online services and updates, the creation of new documents and reports, consultations.
At the same time, on specialized accounting forums, as well as in complaints about procurement, users noted that UA-Budget is also built on the basis of 1C. In particular, LLC Complex Budgetary Systems engages in the implementation and support of this product, which also accompanies the KBS program and the transition to it from the UA-Budget. KBS looks like the same product. It has a common interface and structure with UA-Budget.
There were more contracts ordered for the supply of KBS for budgetary institutions during the full-scale invasion — for more than UAH 5.5 mln. The list includes both licensed updates of the already installed packages, technical support, and granting access to new users.
If not 1C, then Parus
In addition, accountants from the forums note the similarity of the programs UBS (Ukrainian Accounting System) and Parus. The first is positioned as a Ukrainian development, the second is a sanctioned russian accounting program, as well as 1C. By the way, the contact phone number of the company, which is allegedly engaged in the development of UBS, coincides with one of the numbers indicated as the contact of LLC Parus-Ukraine and LLC Parus-Misto.
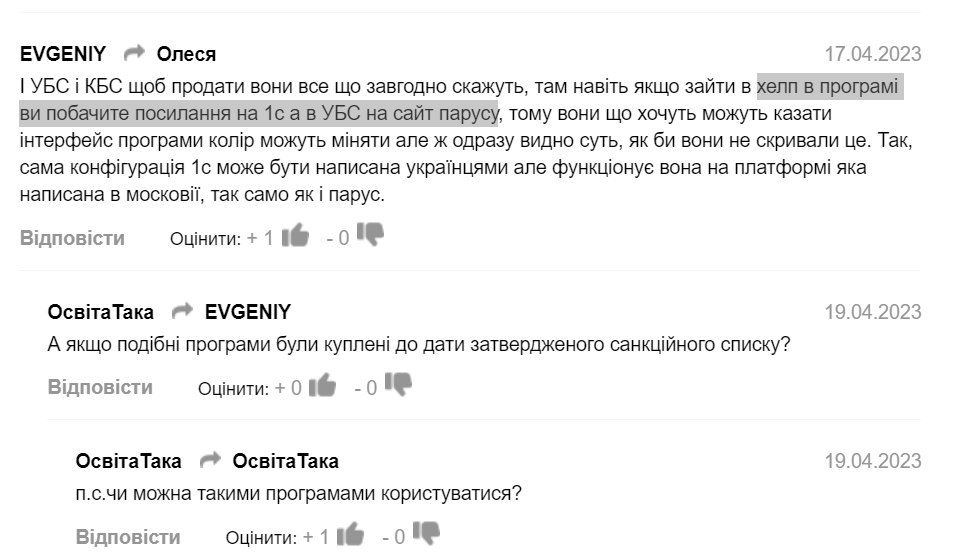
Ukrainian procuring entities concluded contracts for the maintenance of this system for UAH 4.3 mln during the full-scale invasion of russia. Among the services are software administration, technical support, installation, consultations, maintenance, delivery of copies, updating the program.
Ukrainian procuring entities also purchase access to updates from sites on the subdomains 1c.ua and bas-soft.eu. We have found 4 contracts for UAH 55,000, concluded in 2022 and 2023, which provide for access to online services and updates of automated systems located on the sites https://its.1c.ua/ and https://portal.bas-soft.eu/.
Are there any analogues by Ukrainian developers?
As the DOU editorial board noted a year ago, some Ukrainian companies are not ready to abandon the 1C, BAS, UA-Budget, KBS, and other systems because they do not want to reconfigure the established business processes, have already paid a license for a certain time in advance, and the cost of switching to a new product is quite high. In addition, for violation of sanctions restrictions, procuring entities only face a fine. The law does not yet provide for criminal liability.
As explained by Anna Kuts, legal advisor to TI Ukraine, in general, there are two types of restrictions in such cases: regarding the participants and the goods. According to the law, the procuring entity is obliged to reject the bid of the participant if they or their ultimate beneficiary, member, or shareholder is subject to sanctions. If the procuring entity does not do this, they can be fined UAH 25,000 to UAH 51,000. The State Audit Service should identifying such offenses. And the agreement with the entity under sanctions can potentially be declared invalid in court. Similarly, one cannot order goods that are affected by sanctions.
In addition, it is forbidden to purchase something from russians and Belarusians, as well as goods originating from these countries. There is only one exception for origin: if the goods are necessary for repair or maintenance of something that was purchased before October 2022, and it is not sanctioned, one may buy it.
As for the more serious consequences, the Verkhovna Rada has registered draft law No. 8384 dated January 25, 2023, in which MPs propose to introduce criminal liability for failure to comply with, obstruction, or evasion of sanctions. If the draft law is adopted, the upper limit of punishment for these acts will reach 12 years of imprisonment, with the deprivation of the right to hold certain positions or engage in certain activities for a period of 10 to 15 years, or without such, with or without confiscation of property.
However, the lack of Ukrainian analogues is definitely not the reason for the reluctance to abandon the russian software. There are a lot of them.
Back in March 2022, the Opendatabot service and the Netpeak Internet marketing agency created a list of Ukrainian and global companies that can safely replace programs of russian origin. In early 2023, it was somewhat updated and supplemented.
In particular, instead of accounting systems 1C, BAS, UA-Budget, Complex Budgetary Systems, which have a connection with russians, experts offer to use the following:
- UkrainianBimp, Quincefin, Finmap, Pipeliner, Bookkeeper, IT-Enterprise, A2v10, Fintellect, Torgsoft, Ukrsklad, Dilovod, MASTER:Accounting, Fit-budget, IS-Pro, AB OFFICE, Control.Events, Debet Plus, SMARTFIN, UGLA, GMS Office Tools, Masterbuh, Heppy Buh, Limpid Pro, BJet ERP, Komintech.Human resources management, Universal ERP, H-profit, UIS.WMS, Sivers Trade, A5, RemOnline;
- American Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central, SAP;
- GermanAbona ERP.
IS-Pro is the most popular of these. After February 23, 2022, Ukrainian procuring entities concluded contracts for the implementation, expansion, updating, and maintenance of this program for UAH 40 mln on Prozorro. In addition, there are orders for other packages from the list for more than UAH 7 mln.
At the same time, the authors of the selection do not recommend as an analogue another, quite popular Ukrainian development — M.E.Doc. Presumably, because in 2017 this program was hacked, and it let in the Petya virus to the computers of users. Because of this, the work of banking systems and Ukrainian companies was blocked. After the resumption of work, experts noted that the virus could remain even on those computers that were not hacked.
However, according to BI Prozorro, during the full-scale invasion, M.E.Doc packages, updates and maintenance were ordered for UAH 9 mln in Ukraine.
For asset accounting (EAM/CMMS), Netpeak advises the American Champs instead of 1C TSaR.
We asked representatives of several procuring entities to explain why they could not refuse to use programs that have a connection with russian developments. Thus, Olha Dombrovska, accountant of ME Khmelnytskyi City Primary Healthcare Center No.1, noted that she had not seen other substitutes of 1C, except for KBS and BAS. The latter is more convenient for her. It was this product that the medical institution purchased in April 2023.
In addition, Oleksandr Pysymak, legal advisor to the Kyiv enterprise “Specialized Administration of Antislide Underground Works,” referred to the Polish owner of the BAS software:
“As far as we know, the right holder of software products and standard releases (updates) to the software products of the Business automation software (BAS) line, disseminated through the distribution and partner network in Ukraine, is the NetHelp Jarock and Piotr Entrepreneurial Company, established and registered in accordance with the legislation of Poland (location: Lompy, 129, 41-806, Zabrze, Polska, PL; Regon 240691969). Information about the Right Holder is available on the website at https://legalsoft.ua/korystuvacham-program-dlya-avtomatyzatsiyi-biznesu/pro-yurydychno-znachymi-dokazy-maynovykh-prav-pravovlasnyka/. ME SAAUW is not an expert in the field of matching or determining the equivalence of the software specified.”
In March, this ME ordered services for the installation and maintenance of the BAS line for UAH 42,600.
Conclusion
Thus, among the above accounting programs, the procurement of those that are related to the aggressor state or related to its development, makes up a quarter of such orders on Prozorro. This is UAH 15.8 mln of all analyzed contracts in the amount of UAH 72 mln. Such data do not consider contracts concluded without reporting on Prozorro. The amounts can be larger.
The material was prepared within the framework of the USAID/UK aid TAPAS Project/Transparency and Accountability in Public Administration and Services.